Trading involves high risks, please inquire prior to trading
Start trading today, Register here or you can Call +962 6 5548844 , or email [email protected]. Our team is available 7 days a week, 24 hours a day.
Trade with an Award-Winning 25+ Years Group
We've been at the top of our game. Pushing Innovation
and Winning Awards Since 1998
Globally Regulated, Locally Trusted
• Seychelles • London • Larnaca • Beirut • Amman • Port Louis • Dubai • Cairo • Oman
one single Platform giving you countless
opportunities on a Diverse Range of Markets.

FOREX
See how the world's economies react with access to major, minor and exotic currencies from around the globe

STOCKS
They all ring a bell. Trade thousands of US, UK and EU stocks from one single interface

INDICES
You have more than one stock in mind? Not to worry, CFI offers you a variety of indices that would give you the broad exposure you’re looking for
ETF’s
One of the most customisable ways to trade. Explore our range of simple and complex funds and invest towards the future

COMMODITIES
Looking to hedge against economic uncertainties or maybe expecting an increase in the price of Oil? Discover low cost trading on Gold, Oil and other key commodities
Trading Accounts That Suit You
All our clients are V.I.P and so are our accounts type. To make it easier to understand, we've created just two, both fully loaded and both very competitive.
POPULAR
(Per Side Per Lot)




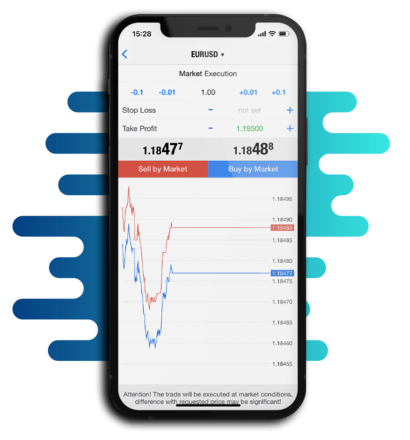
Top-Notch Education, Tools & Analytics
We believe knowledge is the foundation to success This
is why we've created an education & analysis section, to
provide the essential information you need, to help you
progress along your trading journey.






















